Tooth Cyst Removal
The word “cyst” comes from the Greek “pouch” (kystis). And this is not coincidence, because it is a pathological sac-like membrane filled with a liquid, painless until it begins to fester and become inflamed. The cyst is usually situated at the apex of the root.
What are the cyst causes
Dental cysts can be caused due to different reasons. Most often, an infection got into the tooth canal because of untreated caries or a poorly obturated tooth canal serves as a trigger.
If an infection is not promptly treated, a protective capsule is formed to isolate the bacteria accumulation and to prevent pus from spreading. At the early stages, a dental cyst does not bother the patient. At this time, it is up to 5 mm and called a granuloma. Its spread destroys the jawbone tissue. It may cause osteomyelitis or soft tissue phlegmon. Therefore, it should be removed as soon as possible.
Symptoms
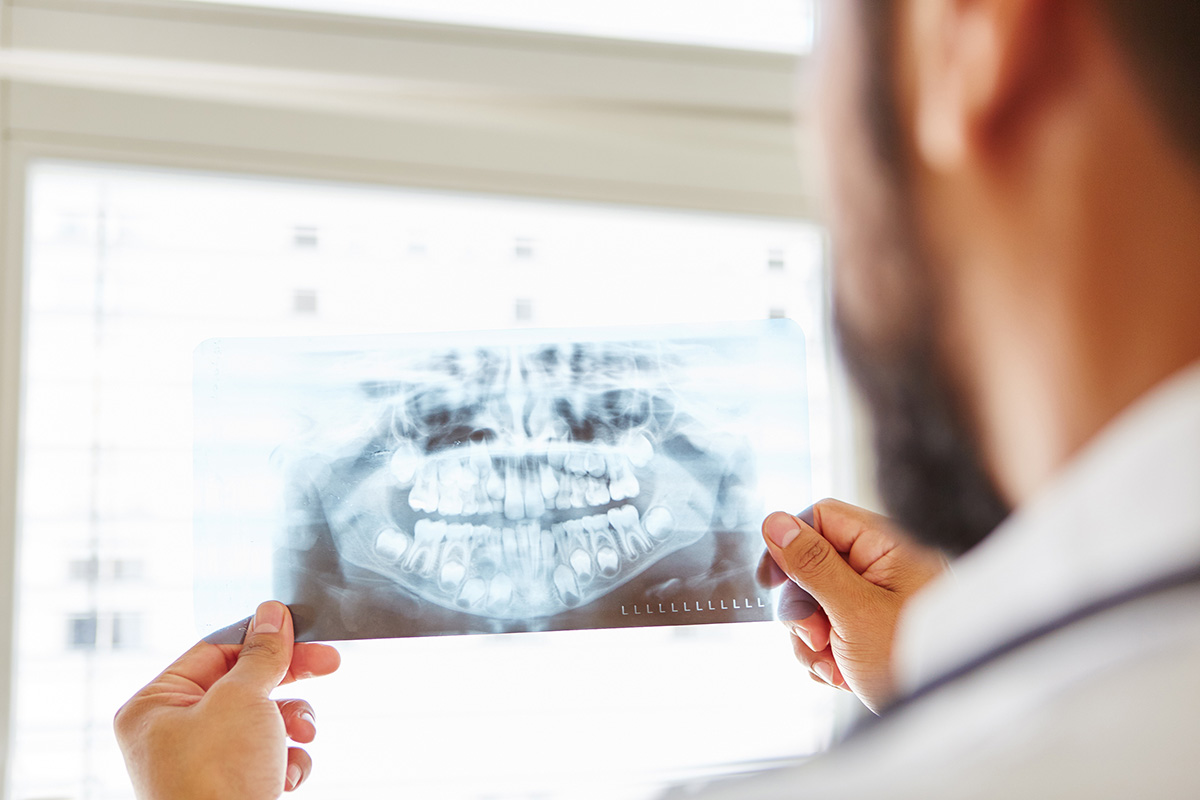
At an early stage, cystic formation does not bother a person. A dental cyst is easily detected in an oral cavity X-ray or even better in a dental tomography. Oval shading with clear edges can be seen in the image.
Indirect signs include tolerable pain when touched, slight tooth displacement.
If a dental cyst is not removed in time, then it begins to grow. The following symptoms can show the growth and further infection:
- gum redness and swelling;
- high temperature;
- pain in the affected area;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Formation may cause different types of periodontitis: granulomatous, fibrous, granulating. An untreated tooth cyst has serious consequences: pus can ooze out into the surrounding tissues, forming a fistula. This often results in antritis (sinusitis). In severe cases, it may cause purulent meningitis, sepsis.
Cyst removal
At the initial stages, conservative therapeutic treatment is applied to the dental cyst, since it is the most sparing. Therapy is possible in a small lesion not exceeding 10 mm.
The surgery removal of the root or periodontal cyst is applied in advanced cases. The surgical method is also indicated in a tooth, to be treated, with a crown or post.
1. Cystectomy
This is a radical method of surgery.
Cystectomy indications:
- cystic formation resulted from the pathology of the odontogenic epithelium;
- a cyst within one or more teeth;
- large overgrowth in the area of the upper jaw and lower jaw.
In this case, an incision is made in the gum, the root tip and cyst are removed. In modern dentistry, retrograde canal is filled with MTA as well. After the surgery, edema is an anticipated sequela for a while. Painful sensations may persist until the wound heals. The procedure is followed by antibiotic prescription.
2. Hemisection
It is performed on multirooted teeth with extensive tissue damage.
Indications:
- root canals cannot be treated;
- dental cavity or root perforation;
- dental cyst inflammation foci in the root divergence (bifurcation) area;
- severe local parodentium diseases.
3. Cystotomy
This is a less traumatic intervention.
This method is indicated in the following cases:
- three healthy teeth in the cyst projection;
- large cysts are localized in the upper jaw with the palatine plate thinning;
- large lesions in the lower jaw with decayed bone tissues.
In this case, the dental cyst is not removed, only its front wall is excised to extract the content, followed by the treatment in order to preserve the tooth. However, the recovery period lasts longer in this method or may even be ineffective.
At Denta Vita we know how to solve the problem in any type and localization of dental cysts. Don’t waste your time. Come to us to keep your teeth healthy and beautiful. Schedule an appointment for an initial examination.